[ad_1]
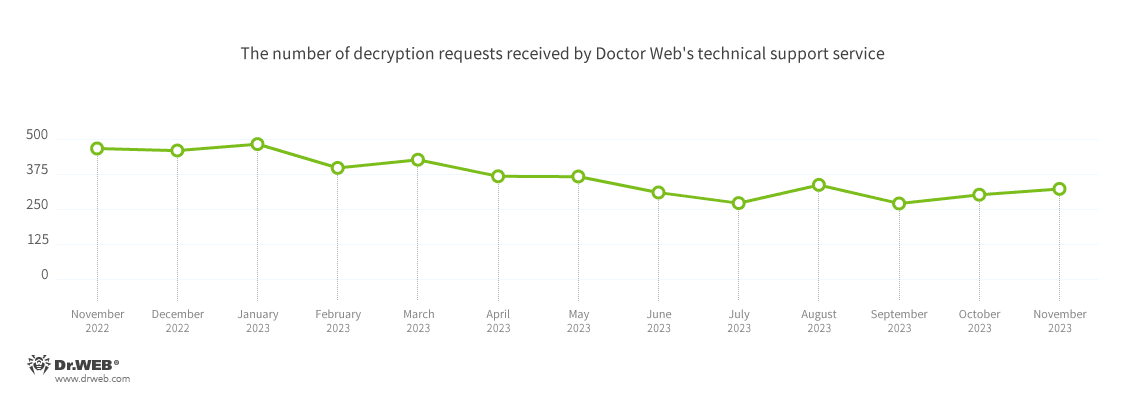
The variety of consumer requests to decrypt recordsdata affected by encoder trojans elevated by 6.98%, in comparison with October. Most frequently, customers encountered Trojan.Encoder.3953, which accounted for 21.70% of all incidents recorded. In 21.20% of instances, customers had been attacked by Trojan.Encoder.26996. With a share of 8.94%, Trojan.Encoder.35534 once more got here in third.
In November, Physician Internet’s malware analysts found new malicious applications on Google Play. Amongst them had been over 20 pretend apps engaged in fraudulent schemes and a trojan that subscribed Android system house owners to paid companies.
Principal traits in November
- A lower within the complete variety of threats detected
- A predominance of phishing paperwork in malicious electronic mail visitors
- A rise within the variety of consumer requests to decrypt recordsdata affected by encoder trojans
- The emergence of recent malicious applications on Google Play
In response to Physician Internet’s statistics service
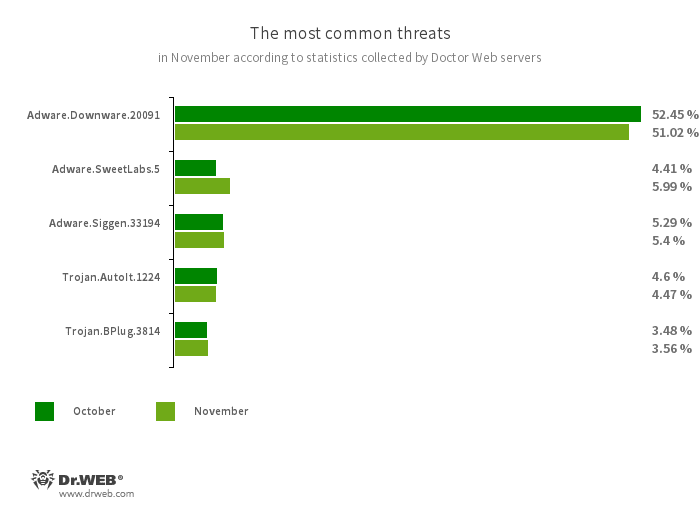
The most typical threats in November:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware that usually serves as an middleman installer of pirated software program.
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternate app retailer and an add-on for Home windows GUI (graphical consumer interface) from the creators of “OpenCandy” adware.
- Adware.Siggen.33194
- The detection title for a freeware browser that was created with an Electron framework and has a built-in adware element. This browser is distributed by way of varied web sites and loaded onto customers’ computer systems after they strive downloading torrent recordsdata.
- Trojan.AutoIt.1224
- The detection title for a packed model of the Trojan.AutoIt.289 malicious app, written within the AutoIt scripting language. This trojan is distributed as a part of a gaggle of a number of malicious functions, together with a miner, a backdoor, and a self-propagating module. Trojan.AutoIt.289 performs varied malicious actions that make it troublesome for the primary payload to be detected.
- Trojan.BPlug.3814
- The detection title for a malicious element of the WinSafe browser extension. This element is a JavaScript file that shows intrusive adverts in browsers.
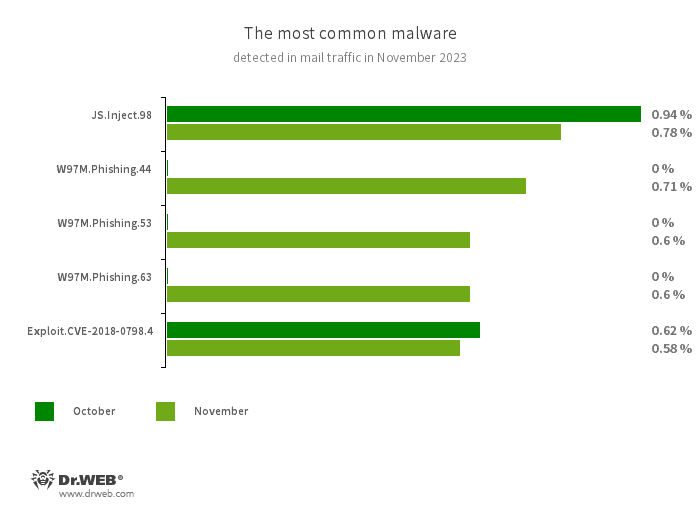
Statistics for malware found in electronic mail visitors
- JS.Inject
- A household of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- W97M.Phishing.44
- W97M.Phishing.53
- W97M.Phishing.63
- Microsoft Phrase phishing paperwork that focus on customers who wish to turn into buyers. They comprise hyperlinks to fraudulent web sites.
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- An exploit designed to make the most of Microsoft Workplace software program vulnerabilities and permit an attacker to run arbitrary code.
Encryption ransomware
In November, the variety of requests to decrypt recordsdata affected by encoder trojans elevated by 6.98%, in comparison with October.
The most typical encoders of November:
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 21.70%
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 21.20%
- Trojan.Encoder.35534 — 8.94%
- Trojan.Encoder.37369 — 3.40%
- Trojan.Encoder.35067 — 2.98%
Harmful web sites
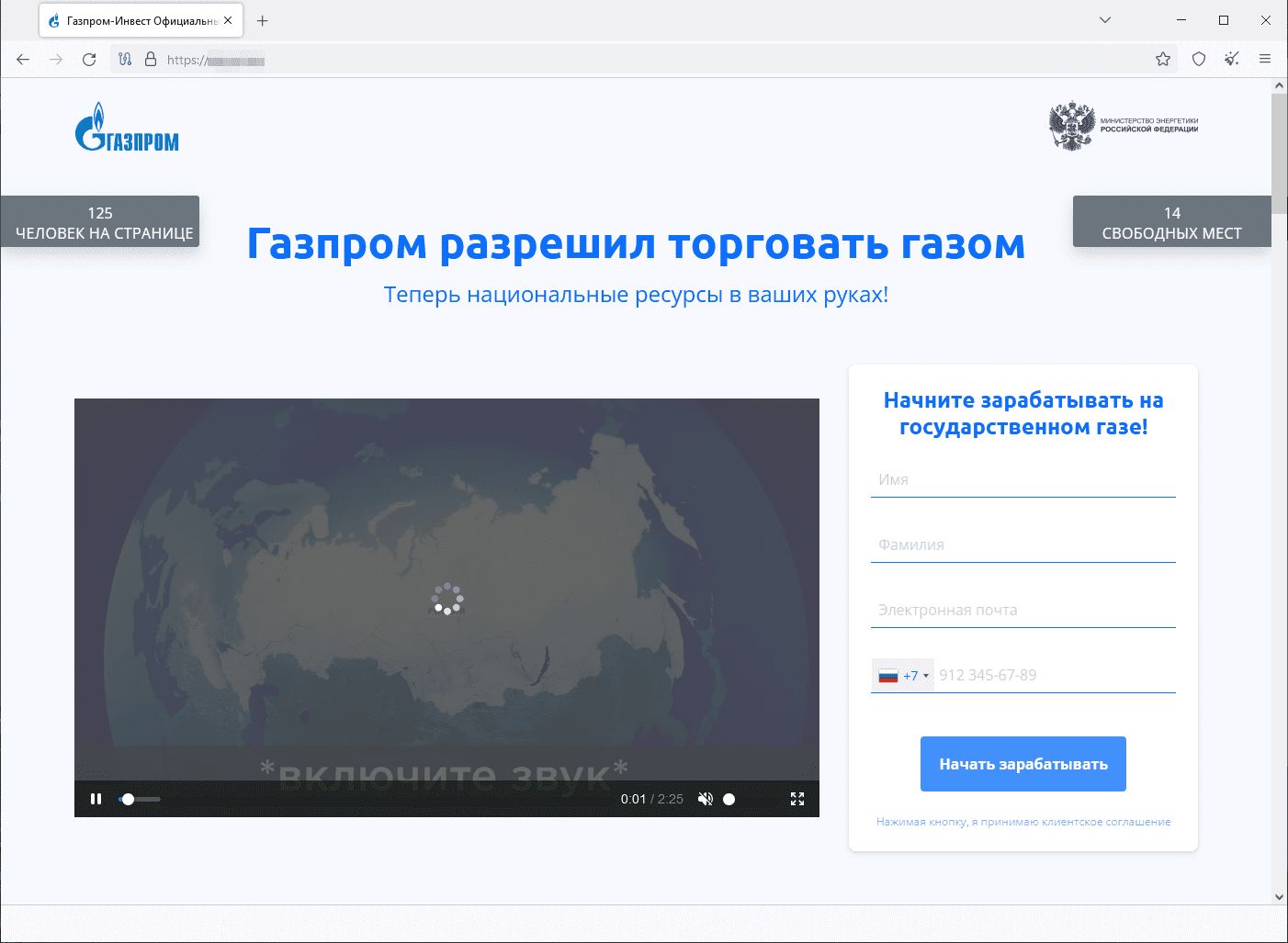
In November, Physician Internet’s Web analysts detected no important adjustments in cyberfraudster exercise. Menace actors once more tried luring potential victims to all types of pretend web sites, amongst which fraudulent funding websites and websites providing “free” lottery tickets and possibilities to take part in prize “attracts” remained the preferred.
Within the case of the previous, customers are inspired to turn into buyers, for which they should present their private information. Within the case of the latter, collaborating in so-called free lottery attracts and on-line contests at all times ends in winnings. To get their prize, customers allegedly must pay a fee.
An instance of a phishing web site the place a customer is invited to turn into an investor:
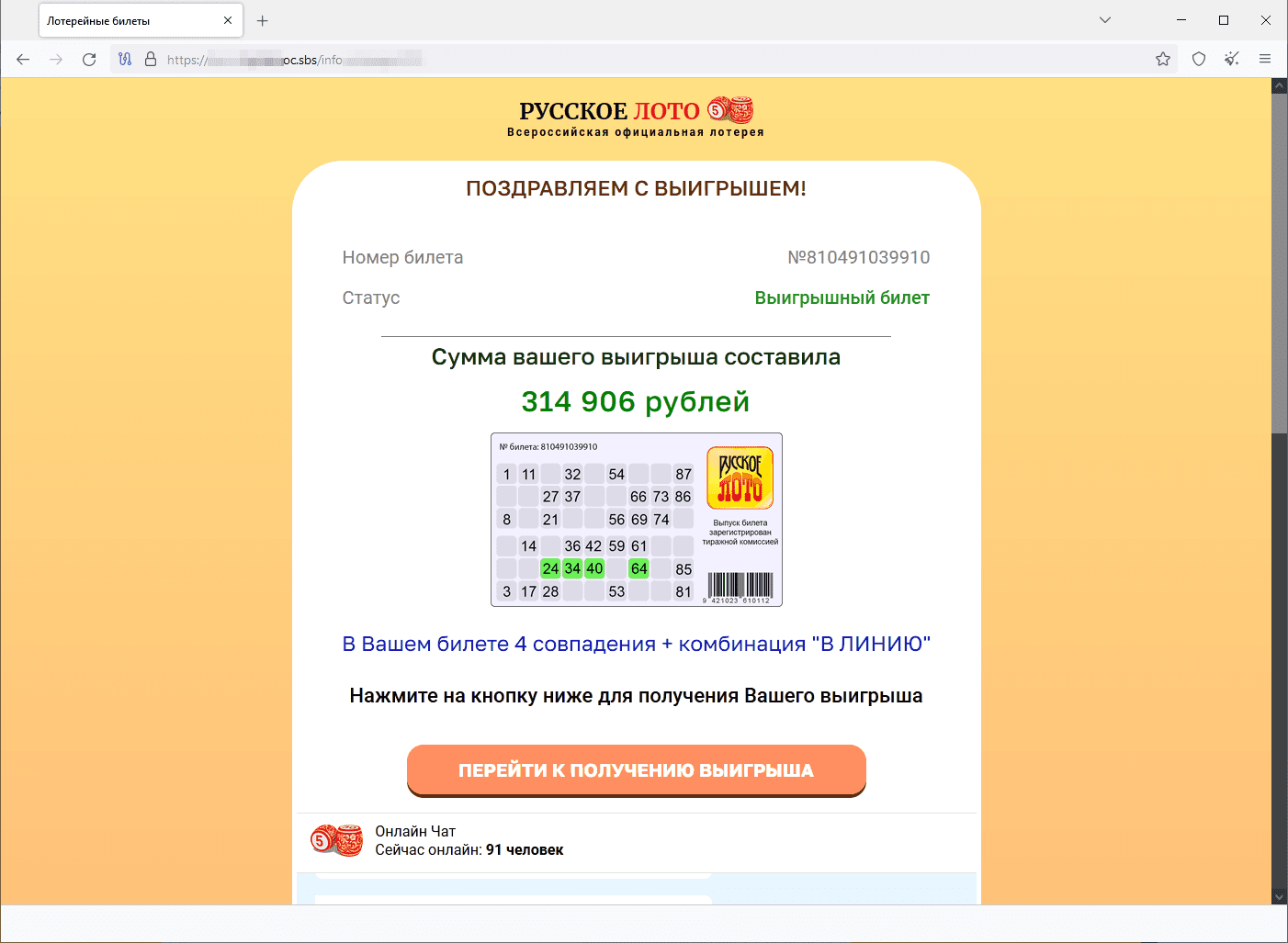
An instance of a fraudulent web site that simulates a lottery drawing:
The consumer allegedly received 314,906 rubles and might go on to obtain their winnings:
Malicious and undesirable applications for cell units
In response to detection statistics collected by Dr.Internet for Android, in November, Android.HiddenAds and Android.MobiDash adware trojans had been detected much less typically on protected units. Furthermore, customers had been much less prone to encounter banking trojans and malicious spy ware applications.
Final month, Physician Internet’s specialists found many new malicious apps from the Android.FakeApp household, which malicious actors deployed to execute varied fraudulent schemes. As well as, the specialists uncovered the Android.Subscription.21 trojan, which subscribed customers to paid companies.
The next November occasions involving cell malware are essentially the most noteworthy:
- A lower in adware-trojan utility exercise,
- A lower in banking trojans and spy ware app exercise,
- The emergence of recent malicious applications on Google Play.
To search out out extra concerning the security-threat panorama for cell units in November, learn our particular overview.
[ad_2]