[ad_1]
A DGA Seeded by the Bitcoin Genesis Block
Edit 2022-08-08: Two weeks after this weblog put up, 360 Netlab printed a detailed report on the malware, whose DGA model 3 I’ve described under. Please learn Netlab’s put up for basic informations concerning the malware and two older DGA’s that’s makes use of. I’ve adopted the identify “Orchard” that they’ve given to the malware.
XMRig is an open-source software program for mining cryptocurrencies like Monero or Bitcoin. It is usually ceaselessly utilized by cryptojacking malware to mine cryptocurrencies on victims’ computer systems. These malwares are a dime a dozen and are principally unremarkable — to the purpose that they continue to be unnamed by AV distributors. Orchard isn’t any exception. What units the pattern aside, nonetheless, is its Area Era Algorithm (DGA) which makes use of two completely different sources for seeding:
- the present date — which is deterministic after all
- stability of the Bitcoin genesis block (the primary block on the Bitcoin blockchain) — which isn’t deterministic
For each seeds the identical algorithm is used to generate the domains. The primary 16 domains are derived from the present date, whereas the following 16 domains are based mostly on the Bitcoin block:
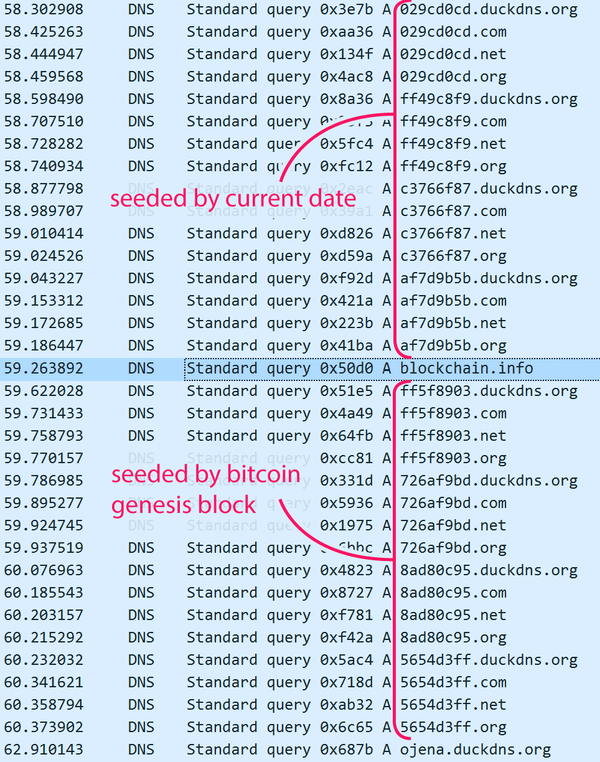
I analyzed the next pattern:
- File kind
- PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Home windows
- MD5
- 077b6b101cccb3d77a98e2cc02003526
- SHA1
- 9e4f04d513ef119d7872c7ce0af6ffbdf4f42a7c
- SHA256
- 2e63bbbbbb11c21445885f85fc8ef398737184c603f365c8e77a8cbf7523cac9
- Dimension
- 507 KB (519680 Bytes)
- Compile Timestamp
- 2022-06-19 16:47:27 UTC
- Hyperlinks
- MalwareBazaar, Cape, Dropping_sha256, Dropping_md5, VirusTotal
- Filenames
- uAAAACCCGGGJ.exe (VirusTotal )
- Detections[
- Virustotal: 53/73 as of 2022-07-22, nothing specific
The sample unpacks to this binary, which — like the original — can be downloaded from MalwareBazaar:
- File type
- PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows
- MD5
- 5c13ee5dbe45d02ed74ef101b2e82ae6
- SHA1
- bdc36bc233675e7a96faa2c4917e9b756cc2a2a0
- SHA256
- ad1e39076212d8d58ff45d1e24d681fe0c600304bd20388cddcf9182b1d28c2f
- Size
- 400 KB (409600 Bytes)
- Compile Timestamp
- 2022-06-19 19:59:36 UTC
- Links
- MalwareBazaar, Dropped_by_md5, Dropping_sha256, Cape, Dropped_by_sha256, VirusTotal
- Detections
- Virustotal: 53/74 as of 2022-07-22, nothing specific.
Many more samples that feature the DGA can be found on VirusTotal since June 22, 2022, with a clear cluster on July 6 and 7. The hashes are summarized in this VT Collection.
Seeding
The first seed is calculated by taking the current date and formatting it as YYYY-mm-dd, e.g., 2022-07-23. Then a hardcoded domain name is appended. In the examined sample, the domain is “ojena.duckdns.org” so the resulting seed string would be “2022-07-23ojena.duckdns.org”.
The second seed is obtained by making a GET request to the following URL:
https://blockchain.info/balance?active=1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa
This url returns the current balance of the Bitcoin genesis block. The response is the seed for the DGA, for example:
{"1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa":{"final_balance":6854870116,"n_tx":3389,"total_received":6854870116}}
Due to the fame of the genesis account, it receives many transactions, which all result in a changed seed string and therefore different domains. The time between transactions varies greatly, but there was only about a 20% chance last year that a domain would have been valid for more than 2 days.
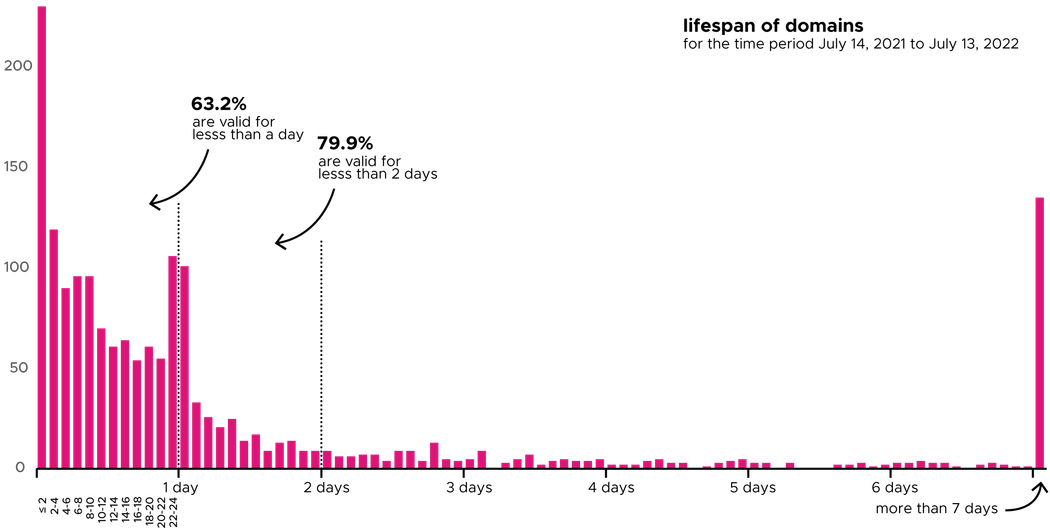
DGAs that use undeterministic sources for seeding are rare: Bedep used the foreign exchange reference rates published by the European Central Bank and Torpig Twitter trends. Unlike for these two examples, the seed in our case can be changed by anyone with a predictable outcome. This allows domains to be registered before they are used by Orchard, something which is not possible for Bedep and Torpig whose seeds can’t be influenced.
Domain Generation
The DGA itself is very simple: The seed string is MD5-hashed, then the hex representation of the hash is split into 4 strings of 8 characters to form the second level domains (sld). These 4 slds are then combined with 4 hardcoded top level domains to form 16 domains:
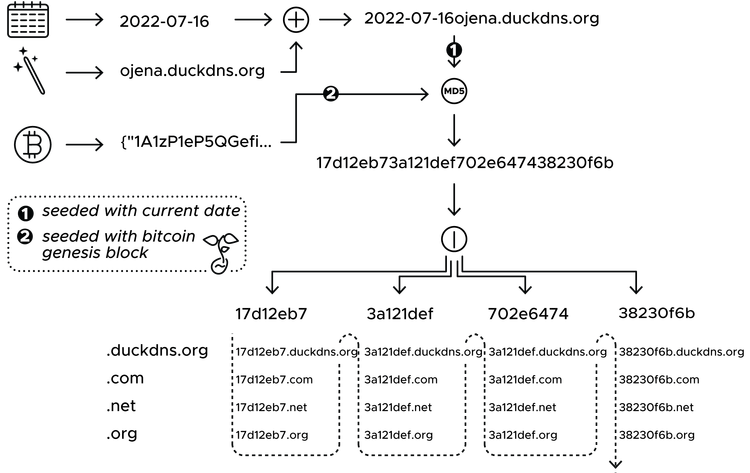
Reimplementation
The following script is a reimplementation of the DGA in Python. It can generate the first set of domains for arbitrary dates, but if you like to generate the second set of domains seeded by the genesis block, you need to request it with the -b command line argument. This will check if the date is covered by a local database of transactions of the Bitcoin genesis block. If necessary, this database will be updated by downloading transactions from blockchain.info. You find the DGA on my Github , along with a database of transactions until September 2022.
import argparse
import hashlib
import itertools
import json
import os
import time
from datetime import date, datetime
from typing import Iterator, Union
import requests
LIMIT = 100
DB_PATH = "db.json"
BLOCK = "1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa"
PATTERN = '{"1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa":{"final_balance":FB,"n_tx":NTX,"total_received":FB}}'
def refresh_blockchain_db():
offset = 0
if os.path.exists(DB_PATH):
with open(DB_PATH) as r:
db = json.load(r)
else:
db = {}
while True:
url = f"https://blockchain.info/multiaddr?active={BLOCK}&limit={LIMIT}&offset={offset}"
r = requests.get(url)
data = r.json()
error = data.get('error')
if error:
print(f"error updating blockchain balance: {data}")
quit()
txs = data["txs"]
for tx in txs:
h = tx['hash']
if h in db:
break
db[h] = tx
else:
time.sleep(1)
offset += LIMIT
proceed
break
with open(DB_PATH, "w") as w:
json.dump(db, w, indent=2)
def get_blockchain_seed(when, up to date: bool = False) -> str:
if when > datetime.now():
elevate ValueError(
"you possibly can't generate the blockchain domains for the longer term!")
with open(DB_PATH) as r:
transactions = json.load(r)
transactions = sorted(
transactions.values(),
key=lambda x: x['balance'],
reverse=True
)
ntx = len(transactions) + 1
for i, transaction in enumerate(transactions):
tt = transaction["time"]
time = datetime.fromtimestamp(tt)
if when < time:
proceed
if i == 0 and not up to date:
""" if the specified date is later than the most recent transaction,
then replace the transaction database to verify it's
the present transaction you wish to entry """
refresh_blockchain_db()
return get_blockchain_seed(when, up to date=True)
stability = transaction['balance']
return PATTERN.change("FB", str(stability)).change("NTX", str(ntx-i-1))
elevate ValueError("the offered date is earlier than the primary transaction")
def dga(when: Union[date, datetime], blockchain: bool = False) -> Iterator[str]:
for i in vary(2):
if i and not blockchain:
return
if i == 0:
magic = when.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
seed = f"{magic}ojena.duckdns.org"
else:
magic = get_blockchain_seed(when)
seed = f"{magic}"
md5 = hashlib.md5(seed.encode("ascii")).hexdigest()
slds = [md5[i:i+8] for i in vary(0, len(md5), 8)]
tlds = [".com", ".net", ".org", ".duckdns.org"]
for sld, tld in itertools.product(slds, tlds):
yield f"{sld}{tld}"
def date_parser(s):
return datetime.strptime(s, "%Y-%m-%d")
if __name__ == "__main__":
now = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="Orchard malware with DGA based mostly on Bitcoin Genesis Block"
)
parser.add_argument(
"-d", "--date",
assist="date for which to generate domains, e.g., 2022-05-09",
default=now,
kind=date_parser
)
parser.add_argument(
"-b", "--blockchain",
assist="additionally generate blockchain domains, requires blockchain db",
motion='store_true'
)
parser.add_argument(
"-u", "--update",
assist="simply replace of blockchain db",
motion='store_true'
)
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.replace:
refresh_blockchain_db()
exit()
for area in dga(args.date, args.blockchain):
print(area)
Traits of the DGA
The next desk summarizes the properties of the DGA
| property | worth |
|---|---|
| kind | TDD-H and TDN-H |
| seeding | time-dependent deterministic and indeterministic |
| technology scheme | hash |
| seed | present date |
| area change frequency | every single day / arbitrary |
| distinctive domains per day | 32 |
| sequence | sequential |
| wait time between domains | none |
| prime degree area | .com, .web, .org, .duckdns.org |
| second degree characters | 0-9a-f |
| regex | “[0-9a-f]{8}.(com |
| second degree area size | 8 |
C2 Communication
The DGA domains — together with the hardcoded area (ojena.duckdns.org) — are used to manage XMRig. First, the consumer sends some fingerprinting info like the next to the C2. The information is shipped unencrypted to a hardcoded port, in my pattern to port 25654:
{
"Active_Window": "*web",
"Antivirus": ["Windows Defender"],
"Authenticate_Type": 0,
"CPU_Model": "twelfth Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-12900K",
"Digicam": false,
"Elevated": false,
"GPU_Models": [
{
"Name": "-",
"Type": 2
}
],
"Id": "F12C8A2EUsernameDESKTOP-XYZ",
"Operating_System": "{"BuildNumber":19044,"MajorVersion":10,"MinorVersion":0,"ProductType":false}",
"Ram_Size": 17179332608,
"System_Architecture": 1,
"Threads": 4,
"Model": 2
}
After that, the XMRig JSON RPC communication can also be despatched — once more unencrypted — to the C2. For instance the login:
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"technique": "login",
"params": {
"login": "CPU",
"go": "x",
"agent": "XMRig/6.15.2 (Home windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) libuv/1.38.0 msvc/2019",
"algo": ["cn/0", "cn/1", "cn/2", "cn/r", "cn/fast", "cn/half", "cn/xao",
"cn/rto", "cn/rwz", "cn/zls", "cn/double", "cn/ccx", "cn-lite/0",
"cn-lite/1", "cn-heavy/0", "cn-heavy/tube", "cn-heavy/xhv", "cn-pico",
"cn-pico/tlo", "cn/upx2", "rx/0", "rx/wow", "rx/arq", "rx/graft",
"rx/sfx", "rx/keva", "argon2/chukwa", "argon2/chukwav2", "argon2/ninja",
"astrobwt"]
}
}
These JSON RPC connections of XMRig might be detected by many Suricata guidelines.
Detection
Talking of detections: there are a lot of YARA rule hits you will notice each on VirusTotal and MalwareBazaar:

Sadly, all these guidelines by The DFIR Report are non practical . I wrote the next YARA rule, but it surely solely matches on the unpacked pattern, e.g., on reminiscence dumps:
rule win_bitcoin_genesis_b9 {
meta:
writer = "Johannes Bader @viql"
date = "2022-07-22"
description = "detects a downloader with a DGA based mostly on the Bitcoin Genesis Block"
tlp = "TLP:WHITE"
model = "v1.0"
hash_md5 = "https://bin.re/weblog/a-dga-seeded-by-the-bitcoin-genesis-block/5c13ee5dbe45d02ed74ef101b2e82ae6"
hash_sha1 = "bdc36bc233675e7a96faa2c4917e9b756cc2a2a0"
hash_sha256 = "https://bin.re/weblog/a-dga-seeded-by-the-bitcoin-genesis-block/ad1e39076212d8d58ff45d1e24d681fe0c600304bd20388cddcf9182b1d28c2f"
strings:
$str_json_1 = ""bytes": ["
$str_json_2 = ""subtype": "
$str_json_3 = "{"bytes":["
$str_json_4 = "],"subtype":"
$str_json_5 = "null}"
$str_json_6 = "<discarded>"
$str_json_7 = "[json.exception."
/*
mov dl, [ebp+var_14]
mov [eax+ecx], dl
mov byte ptr [eax+ecx+1], 0
jmp quick loc_3CBF9F
*/
$split_hash_1 = {8A 55 ?? 88 14 08 C6 44 08 01 00 EB}
/*
inc ebx
cmp ebx, 10h
jl loc_3CBF10
*/
$split_hash_2 = {43 83 FB 10 0F 8C}
/*
push 0
push 0
mov [ebp-14h], edx
mov [ebp-18h], eax
*/
$format_the_date = {6A 00 6A 00 89 55 EC 89 45 E8}
situation:
uint16(0) == 0x5A4D and
all of ($str_json_*) and
all of ($split_hash_*) and
$format_the_date
}
[ad_2]


